Osteochondrosis is the most common cause of back pain.Damage to the intervertebral discs underlying the development of the disease is found in every second person who has reached 40 years of age, and by the age of 50, 70% of the population is already amazing.At the same time, today osteochondrosis is increasingly found in young people and even adolescents.Intervertebral hernia, radicolite, brain supply disorders - all these are complications of osteochondrosis that threaten disability and often leading to disability.
Currently, effective treatment methods that allow not only to remove symptoms, but helping to restore the destroyed areas of the vertebrae, in traditional medicine there is almost no.Therefore, it is so important to understand which factors lead to the destruction of the disks, what needs to be changed in their lifestyle in order to stop the development of osteochondrosis.And what measures should be taken in order to cope with existing changes and launch recovery processes in the spine.
What is osteochondrosis?How is the disease progressing?
Osteochondrosis is a disease in which the processes of destruction in the spinal -motor segment begin to prevail over the processes of recovery, which is manifested by pain in the back, a limitation of mobility, etc.In the course of the development of this disease, intervertebral hernia, radiculitis (radiculopathy), Ishias and other complications can form.
The intervertebral disk (hereinafter referred to as “disk”) is a ring of elastic fabric, the fibers of which are woven into an overlying and underlying vertebra.Due to its special structure, the intervertebral disc protects each vertebra from destruction, and also ensures the mobility of the entire spine (tilments, twisting).
In the center of the intervertebral disk is a pulpic core, which resembles a rubber pillow filled with liquid.In an adult, it consists of 70% water, as well as carbohydrates that can bind and give water.At the time of the load on the corresponding segment of the spine, the core gives the water and flatters, and after the termination of the effect takes the previous form.Such a shock -absorbing pillow allows the spine to spring and extinguish up to 80% of the shock load that comes to the spine.
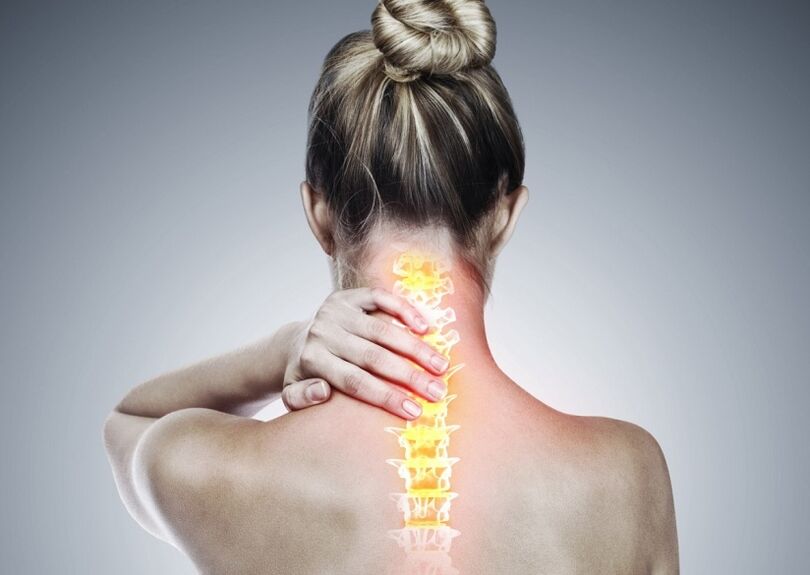
Degenerative-dystrophic processes most often begin with a deterioration in the shock-absorbing function of the intervertebral disc.
- Deterioration of blood supply to the intervertebral disc.In adults, the food of the intervertebral discs is carried out by diffusion: blood is delivered only to the vertebrae, and already through them it “seeps” to the discs.In the best way, the disk is powered during dynamic loads (for example, walking), since the principle of the pump (outflow of the processed fluid when compressed, the flow of nutrients and oxygen when removing the load).Thus, the nutrition of intervertebral discs is difficult especially in the conditions of a sedentary lifestyle (hypodynamia).
- Changes in the pulpic disk nucleus.With a deterioration in blood supply, the supply of water, sugars and amino acids to the pulpoose nucleus is disturbed.Because of this, the production of carbohydrates connecting water suffers.The nucleus is dehydrated, its structure made of gel -like turns into fibrous, the ability to spring and extinguish shots worsens.This increases the load on the fibrous ring and vertebrae, they are more likely to be blocked and injured.
- Changes in the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc.Due to the flattening of the pulpoose nucleus, the increased load lies on the fibrous disc ring.In conditions of poor blood supply, the fibrous ring loses its strength.The instability of the spine occurs, which can lead to the formation of an intervertebral hernia, a displacement of the vertebrae and damage to the spinal cord or nerve roots.
- Disk protrusion.The formation of intervertebral hernia.As the fibers of the fibrous ring weaken, the pulpic nucleus begins to stick out, for example, towards the intervertebral canal (disk protrusion).Such a staggering can further lead to a rupture of a fibrous ring and the formation of a hernia.Read more about the process of formation of intervertebral hernia in a separate article - “Effective treatment of intervertebral hernia at home”.
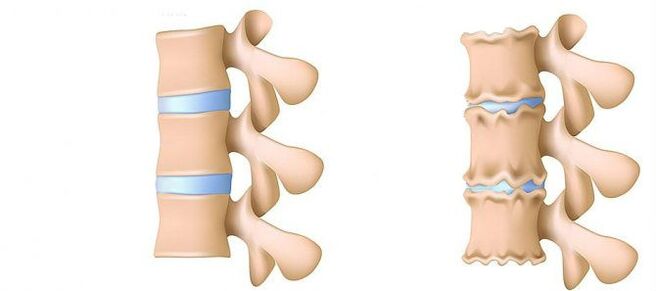
- Spondylosis - the destruction of the intervertebral joints (spondylartrosis), the growth of osteophytes and the ossification of ligaments.In parallel with the formation of intervertebral hernia in osteochondrosis, damage to the intervertebral joints, destructive changes in the vertebra (cartilage) and ligaments are observed.
Since the shock -absorbing function of the intervertebral disc is not performed, the vertebrae and small intervertebral joints begin to constantly be injured.
The instability of the spine is also the cause of damage to the cartilage of the bodies of the vertebrae and articular processes.As a result, bone tissue grows, osteophytes appear(from Greek: osteo - bone, phyto - plant)- Bone growths.The appearance of osteophytes is popularly called the formation of spikes or the deposition of salts.
- Osteophytes can constantly irritate the ligaments of the vertebral segment, which gradually leads to their ossification and to limiting movements in the affected spine.
- Osteophytes can also injure nearby soft tissues, a result of which is the accumulation of dead cells in them, to which the body reacts with inflammation (edema).
- Osteophytes on the surfaces of the vertebrae facing the intervertebral discs damage fibers of the fibrous ring, accelerating the formation of a hernia.The osteophyte, which grows towards the intervertebral canal, enhances the compression of the spinal cord, blood vessels, nerve roots.
- The growth of osteophytes can lead to the wrap of neighboring vertebrae and the complete loss of mobility in the vertebral segment.
Symptoms and signs
Symptoms and signs of osteochondrosis - back pain! Initially, the back pain can occur due to overstrain of the back muscles that try to centrize excessively moving vertebrae (stage 3), so the muscles protect the spinal cord located in the vertebral column.The spinal cord is the central part of the nervous system, so the body tries to prevent its damage (squeezing, irritation).Subsequently, the cause of the pain may already be the vertebrae of the vertebrae, hernial protrusion even with a small size.At the time of the appearance of a hernia, a person, as a rule, feels severe pain (this is what is called cervical or lumbar lader).

Due to the pain in the back, a person involuntarily seeks to take a position in which the intensity of pain decreases - the so -called, forced poses.At the same time, the spine is in a non -violent position that reduces the depreciation abilities of the disks.This increases the risk of their further damage.
As violations progress in joints, the development of ossification of vertebral bodies, articular surfaces and ligaments, the patient's spine begins to lose mobility.Partial, and then complete restrictions on movements in the affected spine.
Complications of osteochondrosis of the spine
There are several stages of development of complications of osteochondrosis of the spine.Their manifestations depend on the department in which the destructive process occurs.
- Discogenic radiculite (radiculopathy), in which the hernial protrusion squeezes the nerve root (a bunch of nerve fibers, extending from the spinal cord and subsequently divided into nerves going to one or another area of the body).The pain is due to both the mechanical effect of hernia on the spine, and the addition of inflammation (edema).
- Vascular-brown syndrome, in which vessels are squeezed that feed the roots of the spinal cord.It is manifested by impaired movements in the hands (with cervical osteochondrosis) or lower extremities (with lumbosacral), as well as a loss of sensitivity.With this complication, the work of internal organs can suffer, to which the affected nerves go (urination, sexual function, intestinal work, etc.) may develop, hypertension may develop and memory deterioration occurs.Sometimes vascular infringement occurs suddenly, with a sharp movement in the affected area of the spine - more often, in the lower back.There is a sharp pain and sudden weakening of the muscles on the affected side - syndrome "paralytic Ishias".
- Violation of the blood supply to the spinal cordcaused by compression of vessels that feed the spinal cord.The extreme degree of complication is an ischemic spinal stroke.The result of this complication is impaired movements in the limbs (paresis, paralysis), loss of sensitivity, deterioration in the work of internal organs up to complete refusal.In some cases, this can lead to the death of the patient, for example, when the renal function seriously suffers.
Symptoms of discogenic radiculitis depend on the spine:
| Location | Symptoms and signs |
|---|---|
| Cervical, cervical-thoracic radiculite | Depending on the level of damage, pain and impaired sensitivity in the neck, shoulder, forearm, fingers occur.Muscle weakness in these departments can also be observed. Often joins neuralgia of the occipital nerves, in which severe pain in the back of the head is noted.Arrhythmia may occur. |
| Lumbar-cross-sized radiculite | It is manifested by pain in the lower back, which is often combined with pain during the sciatic nerve - Ishias, Ishiradiculite.The weakness of the foot muscles also develops, a violation of sensitivity in the thigh, lower legs, and feet may occur. |
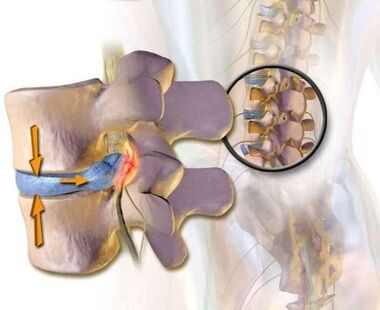
The displacement of vertebral bodies or intervertebral discs with subsequent squeezing of blood vessels and nerve roots may require urgent surgical intervention.
The reasons for the development of osteochondrosis of the spine
Osteochondrosis is called a multifactorial disease - i.e.There can be a lot of reasons for its occurrence.Here we will single out two key factors that gradually lead to the defeat of the intervertebral discs and subsequent changes in the spine:
- Deterioration in the power supply conditions of the intervertebral discs, as well as cleaning their tissues.
- Excessive load on the spine, which leads to the accumulation of dead cells in the tissues of the vertebral segment.
The update of the tissues of the intervertebral discs depends on the sufficiency of blood flow and lymph flow directly to the intervertebral discs, neither blood nor lymph vessels are suitable (which serve in the body to clean tissues).The food and cleaning of the disk is carried out indirectly, that is, slowly.This is the reason that in this area not only quickly occursnutrient deficiency and oxygen starvationbut also quicklyDamaged and dead cells accumulateas well as worked out substances.Cleaning of fabrics from “slags” is necessary, otherwise there will be no place for the occurrence of new functional cells, and then the fabric will gradually lose its function (for example, the pulpoose core of the disk will cease to spring, depreciation and will be sluggishly flattened).
Updating tissues of the intervertebral discs depends on the sufficiency of blood flow and lymph flow.The speed and strength of these processes is influenced by muscle microvibration created (mainly) back muscles during physical stress.In this regard, one of the reasons for the feed and cleaning deficiency is hypodynamia when the back muscles are relaxed or in a static position.
As osteochondrosis develops, blood supply, lymph and venous outflow in the spine can deteriorate due tomuscle spasm.The body gives a signal to the muscles to keep the vertebrae in a certain position relative to each other in the affected area.For a long time, the overstrown muscles squeeze the vessels for a long time, which further exacerbates the situation.
It is obvious to most people that the spine can suffer in the case of an unusual sharp lifting of weights or when injury, however, damage to the spine can be daily and not so tangible in case of violation of the neuromuscular depreciation system.Constant microtraumas in conditions of weak lymph flow lead to the accumulation of dead cells, prevents the growth of functional cells, and further leads to ossification of tissues.
Violation of neuromuscular depreciation as one of the main causes of osteochondrosis

Violation of neuromuscular depreciation as one of the main causes of osteochondrosis in order to reduce the load on the spine when walking, lifting weights, etc.The body has a whole system of neuromuscular depreciation.It is ensured by the functioning of the nervous system of the body and skeletal muscles that interact in agreement to ensure smooth movements and extinguish the shock loads on the bones, joints and, of course, the spine. So, most of the shock loads should extinguish the foot.Also, the muscles of the legs and back are involved in depreciation.If this does not happen (for example, uncomfortable high -heeled shoes do not allow the foot to work), intervertebral discs are subjected to shocks for which they are not intended.The factors that lead to discord in the neuromuscular depreciation system are listed below:
- Violation of posture- Various types of spinal curvatures that prevent him from “springing”, the use of nonphysiological furniture when working in the office, etc.
- Gait violation, running techniques (correctly when running, transfer weight from toe to heel);
- Wearing high -heeled shoes or without heels, which negatively affects the depreciation capabilities of the foot.
- Excessive loads(playing sports, exhausting physical labor), traumatic joints and spine
- Obesity- excess weight shifts the center of gravity of the body, as well as adipose tissue complicates the blood supply to the muscles, the conduct of nerve impulses;
- Driving in transport sitting without depreciation (in a standing position you can spring with your feet);
- Disorders of the function of the nervous system, for example, due to the frequent use of painkillers that negatively affect nervous conductivity.
- Disruption of the kidneysdue to excess forming in the body of decay products.This may be associated with insufficient physical activity - a prerequisite for the work of the lymphatic system, which is responsible for cleansing the tissues from metabolic products and dead cells, as well asliver diseases, chronic foci of inflammationetc.
Hypodynamia
One of the reasons for the widespread osteochondrosis in recent decades is an epidemic of a sedentary lifestyle.The muscles of the back and the press in ordinary life are not involved enough and quickly weaken, and strong muscles are needed for the health of the spine that are not overloaded with static tension, but are busy with dynamic work.The muscles of the back are the most quickly weaken with hypodynamia, which is fraught with the following consequences:

- Insufficient support of the spine in careless movements, which leads to overloading the intervertebral discs, the displacement of the vertebrae and the occurrence of intervertebral hernias.
- Deterioration of blood supply to the spine: the dynamic work of skeletal muscles is a prerequisite for blood flow to any organ, including the spine.As a result of insufficient operation of the muscles of the back, destructive changes in the intervertebral discs progress - cells die from a deficiency of nutrients and oxygen.And dead cells accumulate, interfering with restoration.
- Deterioration of lymph flow and venous outflow, which leads to the accumulation of dead cells in the tissues.The work of the skeletal muscles is especially important for the work of the lymphatic system, since most of its vessels (for example, lymphocapillaries) do not have muscle walls, and “pushing” of the lymph in blood vessels depends on the work of skeletal muscles.
4 principles of effective treatment
In order not only to remove the symptoms, but to cope with the cause of the development of osteochondrosis, spondylosis, radiculitis and Ishias, the following tasks need to be solved:
- Create opportunities for cleansing tissues from dead cells.This is a necessary condition for recovery in order to impede the further formation of osteophytes and free the space for tissue regeneration.To do this, restore/strengthen the lymph flow and venous outflow from the affected segments;
- Enhance blood supply to the affected area;
- Improve the tone of all muscles supporting the spine.This will allow:
- create conditions for stimulationownblood flow and lymph flow in the spine;
- Restore the operation of the neuromuscular depreciation system, which is necessary for adequate support for the spine, to prevent new damage.
- Eliminate pain, becauseThis will give an opportunity:
- Remove muscle clamps that block blood flow to the spine;
- Avoid the forced poses.
Medication (medicinal) therapy
Today, in the treatment of osteochondrosis and its complications, drugs of the following groups are used:
- NECEPOID anti -inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)- in the form of tablets or injections of drugs.These funds have the ability to reduce pain, reduce the activity of inflammation.However, the effect of their use does not last long - from several hours to two to three days.Therefore, such funds must be taken for a long time - weeks, and sometimes months.At the same time, these drugs negatively affect the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.Their long -term reception is fraught with the development of gastritis, ulcerative lesions.In addition, they can negatively affect the work of kidneys, liver, and contribute to the development of hypertension.And, at the same time, these funds do not contribute to the cleansing of discs from dead cells.Therefore, their use is only a way to relieve symptoms for a while, but not to eliminate the main problem.
- CTEPOID (gopmonal) anti -inflammatory drugs.As a rule, they are used for severe and impenetrable pains accompanying hernia, radiculitis, Ishias, etc. Gopmons have the ability to eliminate manifestations of inflammation (due to oppression of the immune system), relieve pain.But they also negatively affect the mucous membranes of the stomach and intestines, promote leaching of calcium from bones, inhibit the production of their own GOPMONs.And do not contribute to cleansing the focus of dead cells.
- Papasmolics- drugs that affect the muscles or nerves that go to the muscles, and cause relaxation of skeletal muscles.These means help to relieve muscle clamps for a while, reduce pain and improve blood flow.But at the same time, they do not help cleanse tissue from dead cells.Therefore, they do not contribute to cure for osteochondrosis.
- Epiduvision blockade- the introduction of painkillers and gopmonal agents into the space between the solid brain shell and the periosteum covering the vertebrae.It is used, as a rule, for intense pains - in the acute period of the intervertebral hernia, with severe radiculitis, Ishias.Depending on the composition, such an injection helps relieve pain for a period of several hours to several days.After the expiration date, the manifestations of the disease are returned, becauseThe procedure does not help restore metabolic processes in discs.In addition, when it is carried out, there is a risk of injury to blood vessels and nerves.

As osteochondrosis and the development of complications progressyou have to resort to medication more and more often, increase dosage.This leads to high financial costs, as well as further deterioration in health due to side effects of drugs.
Drug therapy, as a rule, is supplemented by immobilization of one or friend of the spine using orthopedic corsets of varying degrees of stiffness.